Python in Gitpod
Gitpod comes with great support for Python built-in. Still, depending on your project, you might want to further optimize the experience.
Python Project Examples
Before we get started, here are some examples of already-gitpodified repositories!
| Repository | Description | Try it |
|---|---|---|
| python-flask-api-tutorial | A step by step Todo List API tutorial with Flask + Python | |
| django-locallibrary-tutorial | An example website written in Django by MDN | |
| Gitpod-PyQt | A PyQt example for Gitpod | |
| wxPython-example | A wxPython example for Gitpod |
Python Versions
Run pyenv versions to see which Python versions are pre-installed in Gitpod.
The easiest way to install a new Python version is to use pyenv install <VERSION>. For example, suppose you wanted to install Python 3.6.4, you would run pyenv install 3.6.4.
You can switch between Python versions using pyenv local <VERSION>. For example, if you wanted to switch to Python version 2.7.17 you would run pyenv local 2.7.17. This will create a .python-version file that controls which Python version is the default in your project. (Note: When running it in a Dockerfile, replace local with global to change the system default.)
Start tasks
You can start building your project when, or even before you start your Gitpod workspace. Are you using a requirements.txt file to manage dependencies? If so, add this to your .gitpod.yml to automatically pre-install all dependencies when starting a workspace:
tasks:
- init: pip3 install -r requirements.txt
command: python3 main.pyLinting
You can create a setup.cfg or a pycodestyle.cfg in the project root and adjust pycodestyle rules there like this:
[pycodestyle]
ignore = E226,E302,E41
max-line-length = 160
statistics = TrueYou’ll need to refresh the browser in order to update these rule. Source.
VSCode Extensions
While the most popular Python VSCode extensions are built into Gitpod, here are a few “nice to have” extensions that you can use as well.
ARepl for Python
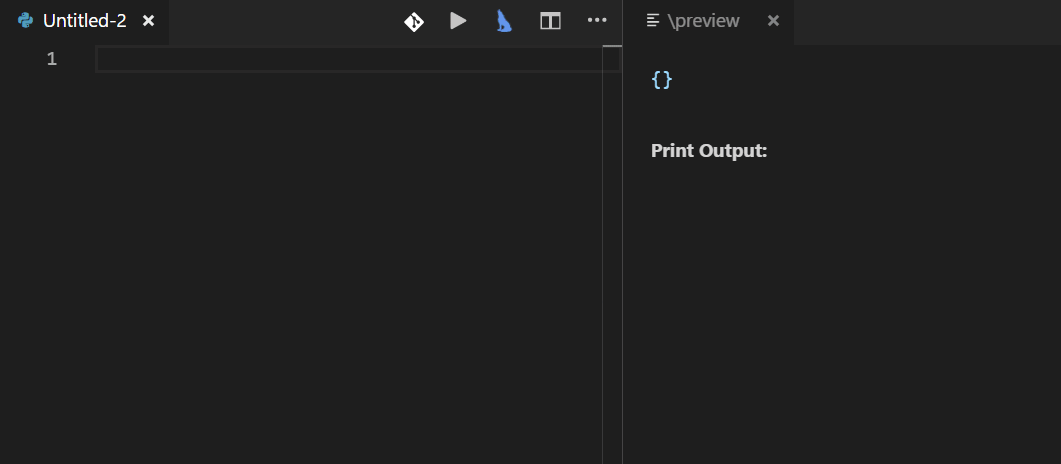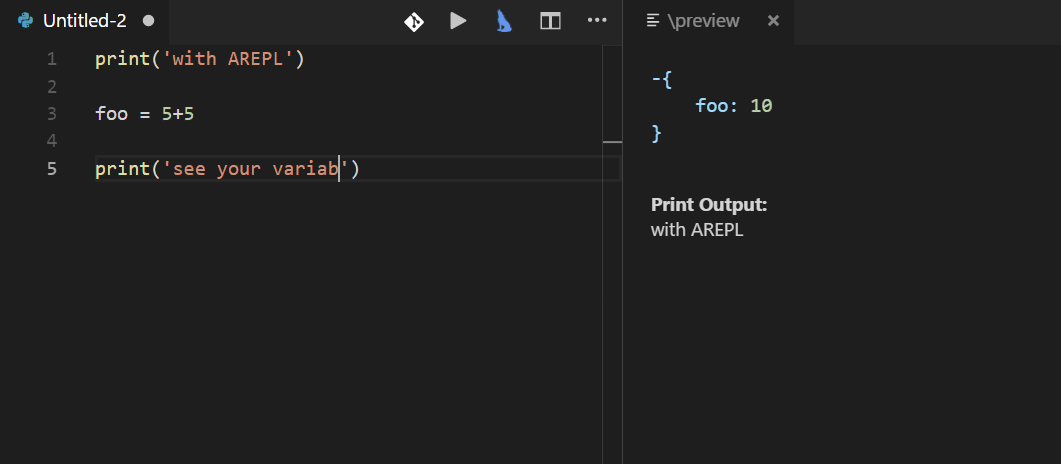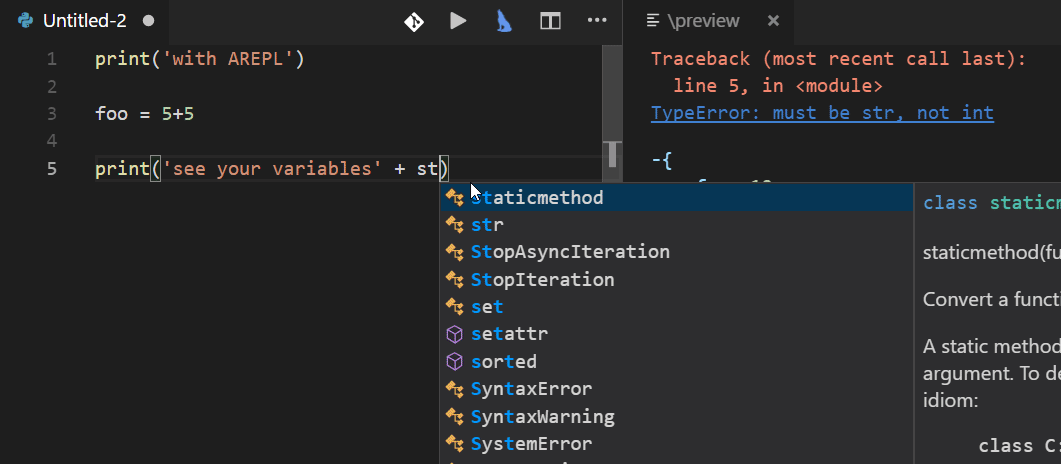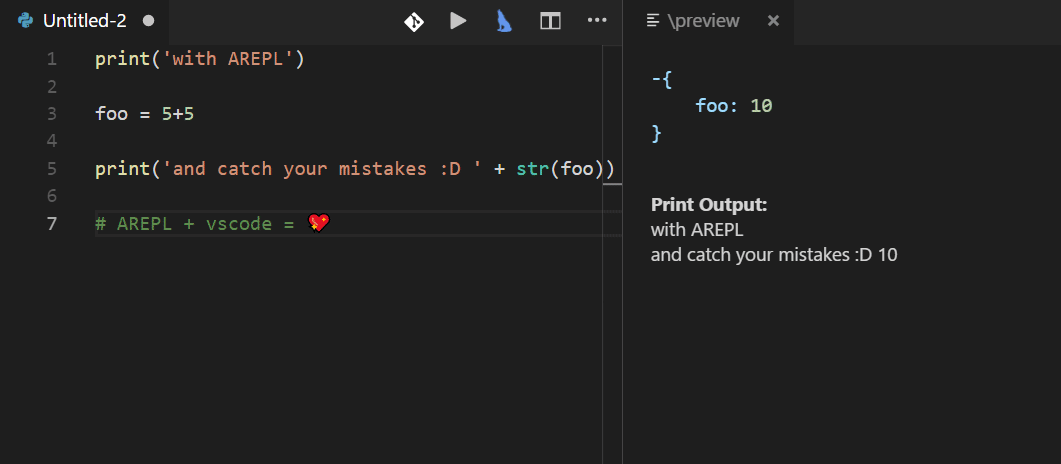 ARepl for Python is helpful for constantly checking your code and debugging.
To install this extension for your repository, add the following to your .gitpod.yml:
ARepl for Python is helpful for constantly checking your code and debugging.
To install this extension for your repository, add the following to your .gitpod.yml:
vscode:
extensions:
- almenon.arepl@1.0.20:Uu7lIOwyLgmNWpTwCl/iqQ==Python Test Explorer
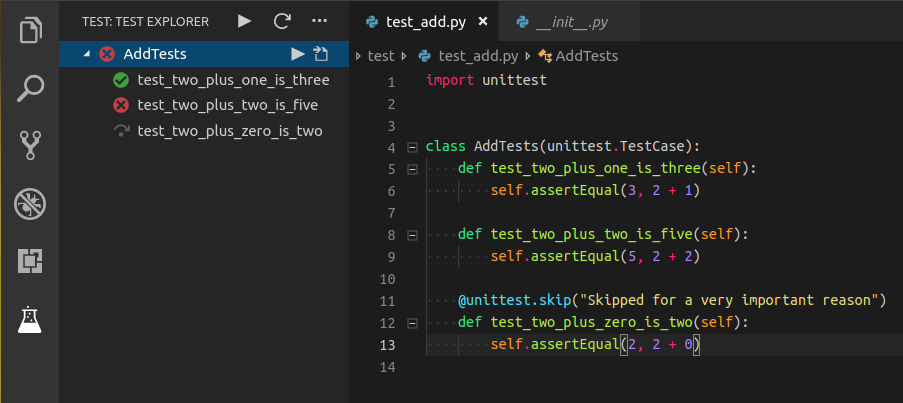 Easily test your python extensions with the Python Test Explorer.
To add this to your repository add the following to your .gitpod.yml
Easily test your python extensions with the Python Test Explorer.
To add this to your repository add the following to your .gitpod.yml
vscode:
extensions:
- littlefoxteam.vscode-python-test-adapter@0.3.16:tZ/6xOSSdKUaq6JCUVkD+A==GUI Applications with wxPython
To install wxPython to your repository please add the following to your .gitpod.Dockerfile. If you don’t have one, simply run gp init and commit the two generated files.
# This will pull the official Gitpod `vnc` image
# which has much of what you need to start
FROM gitpod/workspace-full-vnc
USER gitpod
# Install wxPython dependencies
RUN sudo apt-get -q update && sudo DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq freeglut3-dev python3.7-dev libpython3.7-dev libgl1-mesa-dev libglu1-mesa-dev libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgtk-3-dev libnotify-dev libsdl2-dev libwebkit2gtk-4.0-dev libxtst-dev libgtk2.0-dev && sudo rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Install wxPython
RUN pip3 install -U -f https://extras.wxpython.org/wxPython4/extras/linux/gtk3/ubuntu-18.04/ wxPythonHere is a corresponding .gitpod.yml example:
image:
file: .gitpod.Dockerfile
# This will expose all necessary ports needed for your VNC image
ports:
- port: 6080
onOpen: open-preview
- port: 5900
onOpen: ignore
- port: 35900
onOpen: ignore
# This will make it so that on workspace start it will run a file called `app.py`
tasks:
- command: python3 app.pyWe also support other GUI frameworks such as `Kivy` and `PyQt`
Here are some other examples of Python GUI applications in Gitpod:
| Name | Framework | Try it |
|---|---|---|
| Tic-Tac-Toe-GUI | Kivy | |
| Pong | Kivy | |
| Gitpod-PyQt | PyQt |
Debugging
Here is a quick clip on how to automatically configure debugging for Python!
So, basically in this video we:
- First, open the Python file that we want to debug
- Then, go to the debug menu and select “Add Configuration…”
- Next, in the dropdown choose “Python”
- Next, choose “Python File” as the debug configuration
- Finally, start debugging your Python program!
You can also create the Python debug configuration file manually
To start debugging your Python application in Gitpod, please create a new directory called .theia/, and inside add a file called launch.json, finally, add the following to it:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Python: Current File",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${file}",
"console": "internalConsole"
}
]
}Then, simply open the Python file you want to debug, open the Debug panel (in the left vertical toolbar, click the icon with the crossed-out-spider), and click the green “Run” button.
To see a basic repository with Python debugging enabled, please check out gitpod-io/Gitpod-Python-Debug:
Pandas
Welcome data scientists! This part of the guide will show you how to configure Gitpod for Pandas development.
Try Pandas in Gitpod
To see a minimal project with Pandas installed and configured, please check out gitpod-io/Gitpod-Pandas:
Further Reading
- VSCode documentation for Python debugging All the information there should also apply to Gitpod as well.
- Troubleshooting Matplotlib/TK Here is how to troubleshoot Matplotlib/TK issues for Python GUI applications.
- Debugging Django This is how to debug Django applications in Gitpod.